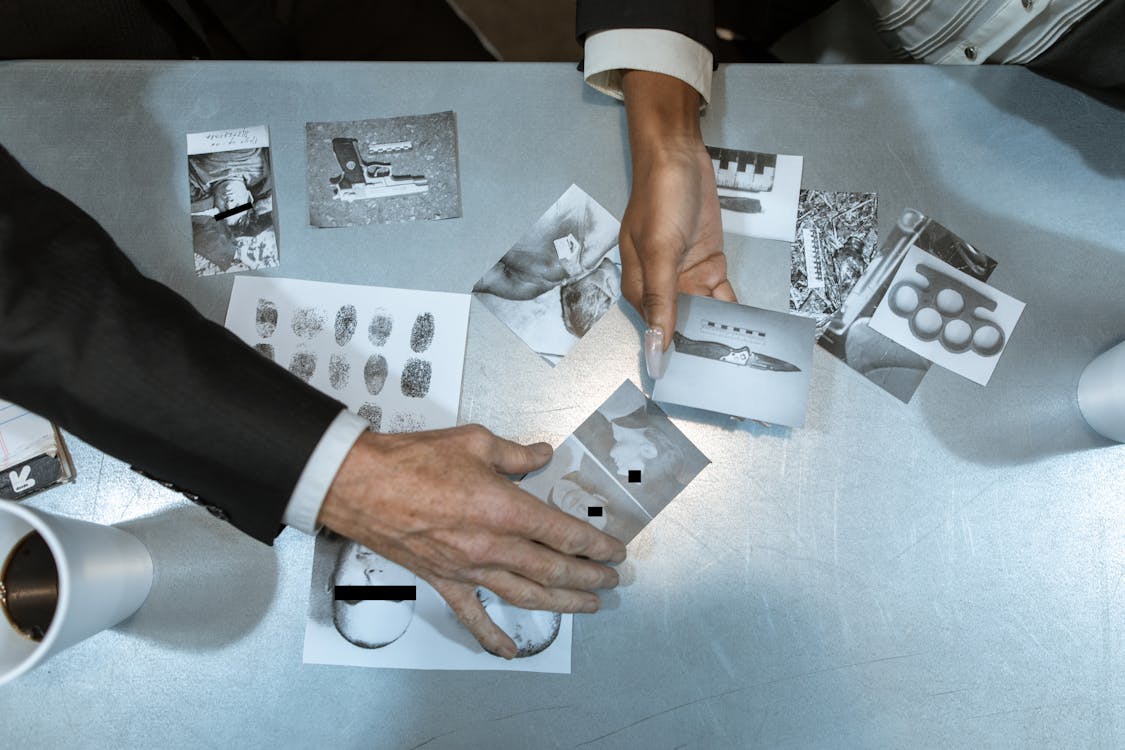
In today’s justice system, digital evidence plays a critical role in shaping verdicts. From text messages to location logs, smartphones and computers hold powerful clues. Yet technology alone cannot speak for itself in a courtroom. This is where the human element becomes essential. Through forensic data interpretation, analysts bridge the gap between raw digital artifacts and real-world meaning.
Judges and juries rely on expert interpretation to understand what the evidence reveals—and just as importantly, what it doesn’t. This combination of technical expertise and human reasoning makes forensic analysts indispensable in modern legal proceedings.
From Raw Data to Meaningful Evidence
Digital devices generate enormous amounts of information—metadata, timestamps, deleted files, and communication records. To the untrained eye, these raw data points mean very little. But forensic analysts know how to decode them into narratives that courts can understand.
For example, a forensic computer analyst might identify internet activity hidden deep within system files. Combined with supporting logs, this data can provide insight into whether an individual’s online actions were deliberate or accidental. Similarly, consultants offering digital forensic services help law firms and investigators recover and interpret information in ways that remain reliable under courtroom scrutiny.
The Role of Context in Data Analysis
Data without context can mislead. Analysts, therefore, examine surrounding circumstances to make sure evidence tells a complete and accurate story.
Take the case of a text message. Its content may seem incriminating, but experts dig deeper into delivery status, device ownership, and patterns of communication. Context distinguishes a genuine message from one that may have been spoofed or misattributed.
This careful consideration is why lawyers often turn to computer forensics consultants and cyber forensic experts. These specialists have the skills to evaluate whether evidence is trustworthy, relevant, and fairly represents the actions of the individual involved.

Establishing Authenticity of Digital Evidence
One of the most important tasks of forensic analysts is proving the authenticity of digital evidence. Courts require assurance that a file, recording, or document hasn’t been altered or tampered with.
Techniques such as cryptographic hashing and chain of custody documentation help establish integrity. In addition, analysts rely on tools like authentic audio forensics or video forensics to confirm that multimedia evidence remains in its original form. A manipulated voicemail, for instance, can shift the meaning of a case entirely—making proper verification essential.
By focusing on authenticity, forensic professionals provide courts with evidence that can withstand challenges from opposing counsel.
Explaining Complex Evidence to Courts
Not everyone in a courtroom has technical training. Judges and juries may struggle to understand the nuances of digital investigations. That’s why analysts must act as interpreters, translating their findings into clear, accessible explanations.
A forensic computer expert might explain internet browsing history by showing how timestamps connect to real-world actions. Similarly, a forensic computer analyst can simplify complex system logs into straightforward timelines that illustrate intent.
This ability to communicate effectively ensures that digital evidence doesn’t just exist in reports—it becomes understandable and meaningful for the people making legal decisions.
Forensic Analysts as Storytellers
More than technicians, forensic analysts are storytellers. They weave together fragmented pieces of digital evidence into coherent narratives that courts can grasp.
Consider a case involving GPS logs, call histories, and deleted texts. By applying forensic cell phone data recovery, an analyst can reconstruct a timeline of movements and communications. This narrative might confirm or challenge eyewitness accounts, painting a clearer picture of events.
Storytelling is what makes analysts invaluable. Without it, evidence risks being reduced to isolated facts without context or connection.
Bridging the Gap Between Technology and Human Behavior
Digital artifacts—such as keystrokes, deleted files, or surveillance footage—are only meaningful when tied to human actions. Analysts bring the technical and human together, asking critical questions: Did a user intentionally erase data? Was the suspicious behavior caused by an error or deliberate planning?
Specialists in video forensic services and mobile device forensics often analyze access logs and timestamps to determine intent. Meanwhile, a video enhancement expert may clarify blurred security footage to establish whether a suspect can truly be identified.
Through this process, forensic experts transform technical details into evidence that reflects real-world behavior, ensuring the justice system can fairly weigh digital proof.

Collaboration with Legal Teams
Forensic analysts rarely work alone. They collaborate closely with attorneys, investigators, and law enforcement to ensure evidence is interpreted correctly and presented persuasively.
For example, forensic audio services may be used to evaluate a threatening voicemail. Once the audio is clarified and verified, lawyers rely on the analyst to explain its meaning in court. Similarly, audio forensic services can uncover nuances in recordings—such as background noise or speaker identification—that strengthen or weaken a case.
This partnership ensures that attorneys present evidence confidently, and that judges and juries receive a balanced, accurate view of digital findings.
Recognizing the Limits of Forensic Analysis
While forensic analysts provide powerful insights, they are also responsible for acknowledging limitations. Devices may be corrupted, data incomplete, or evidence hidden behind strong encryption.
In such cases, honesty and transparency protect the credibility of the investigation. A forensic video analysis expert might explain that poor camera resolution makes identification uncertain, while an audio forensic expert may testify that environmental noise limits the clarity of a recording.
By recognizing boundaries, forensic professionals protect the integrity of their work and ensure that courts don’t overestimate what technology can achieve.
Expert Testimony in the Courtroom
The role of forensic analysts extends beyond examining data; they must often serve as expert witnesses. In court, they face cross-examination, where every detail of their findings is challenged. Their ability to remain composed and defend their methods is critical to ensuring that digital evidence maintains its credibility.
For instance, a digital forensic consultant may be asked to explain the methods used in a cell phone searching case. They must describe not only what was discovered—such as deleted call logs or encrypted chats—but also how the evidence was preserved. This helps judges and juries understand the reliability of the process.
Because digital artifacts can easily be disputed, analysts’ testimony often determines whether evidence is accepted or dismissed. Their clarity, impartiality, and expertise reinforce the connection between data and truth.

Balancing Objectivity and Interpretation
While analysts are expected to interpret evidence, they must do so without bias. Courts rely on objectivity, so personal assumptions must never cloud the analysis. Instead, experts rely on tested methodologies, validated tools, and repeatable processes.
For example, digital video forensics can be used to examine surveillance footage in a robbery investigation. If the analyst adjusts brightness or applies filters to clarify the image, they must explain the process step by step. Similarly, in cases requiring audio forensics, professionals must show that their methods did not introduce changes that could alter meaning.
This strict objectivity ensures that forensic data interpretation remains a reliable foundation for justice.

Case Studies: Human Insight in Action
Real-world cases illustrate how analysts bring human reasoning to digital findings. Consider a corporate fraud investigation where large volumes of emails were recovered. While the sheer number of messages might overwhelm a jury, analysts highlighted patterns in communication that revealed intent to deceive.
In another case, forensic cell phone data recovery revealed a deleted string of texts that placed a suspect near a crime scene. The analyst explained not only the recovery process but also the timing and context, showing how digital trails aligned with physical evidence.
These examples demonstrate how experts transform overwhelming technical data into focused, persuasive narratives. Without their human insight, digital findings risk becoming meaningless numbers on a screen.
The Evolving Role of Analysts
As technology advances, so too does the role of forensic professionals. Artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and encrypted messaging apps create new challenges for data recovery and interpretation. Analysts must continually adapt, staying ahead of techniques used to hide, alter, or obscure evidence.
Modern cases often involve mobile device forensics, where analysts extract data from encrypted applications or recover files from damaged hardware. Others require forensic video services, which use advanced tools to analyze security footage from multiple sources.
This evolution underscores a key truth: while technology changes, the need for human interpretation remains constant. Machines may process data, but analysts provide the judgment and reasoning that courts depend on.

Preparing Courts for the Future
Looking ahead, forensic analysts are likely to play an even greater role in bridging technology and justice. With the growth of cybercrime and digital fraud, courts must be prepared to handle increasingly complex technical evidence.
Training for judges and attorneys is already becoming more common, helping them understand the basics of digital investigations. However, it is forensic professionals who ultimately guide them through the complexities of cases. Whether explaining audio forensic services or analyzing system logs from corporate networks, experts ensure evidence is interpreted fairly and accurately.
As society continues to generate more digital data, forensic data interpretation will remain a vital link between human behavior and legal accountability.
Why Choose Eclipse Forensics
At Eclipse Forensics, we understand that evidence is only as strong as its interpretation. Our team brings decades of experience in bridging digital data with courtroom reality. Whether you need digital forensic services, forensic audio services, or advanced video forensic services in Florida, we deliver insights that stand up to scrutiny.
We know that every case is unique, which is why our cyber forensic experts and computer forensics consultants work closely with attorneys and investigators to uncover the truth. From mobile device forensics to authenticate audio forensics, our specialists ensure that data is not only recovered but also explained clearly, accurately, and credibly.
When evidence becomes the cornerstone of your case, you need a partner who can translate complex findings into courtroom-ready narratives. At Eclipse Forensics, we don’t just analyze data—we help you win trust, strengthen arguments, and secure justice.
Contact us today.